

Inhibition of pathways of synthesis of other important mediators, such as leukotrienes, are currently under investigation and may provide another approach for the development of new therapeutic agents. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis can, therefore, account for most of the therapeutic as well as toxic effects of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by these drugs accounts for many of their major toxic effects, including gastritis, which is the most common side effect precipitation or aggravation of renal failure fluid retention hyperkalemia antiplatelet effects with hemorrhagic phenomena and aggravation of asthma and rhinosinusitis. Latanoprost reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through the uveoscleral pathway, which is the principal site of action of prostanoids. 7 Furthermore, because at least some prostaglandins improve uveoscleral outflow, these. Latanoprost is a prostaglandin F-2 alpha (FP) analog that is used in to reduce intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma. Siu Ling Wong, Wing Tak Wong, Xiao Yu Tian. 1 The risks associated with these methods include.
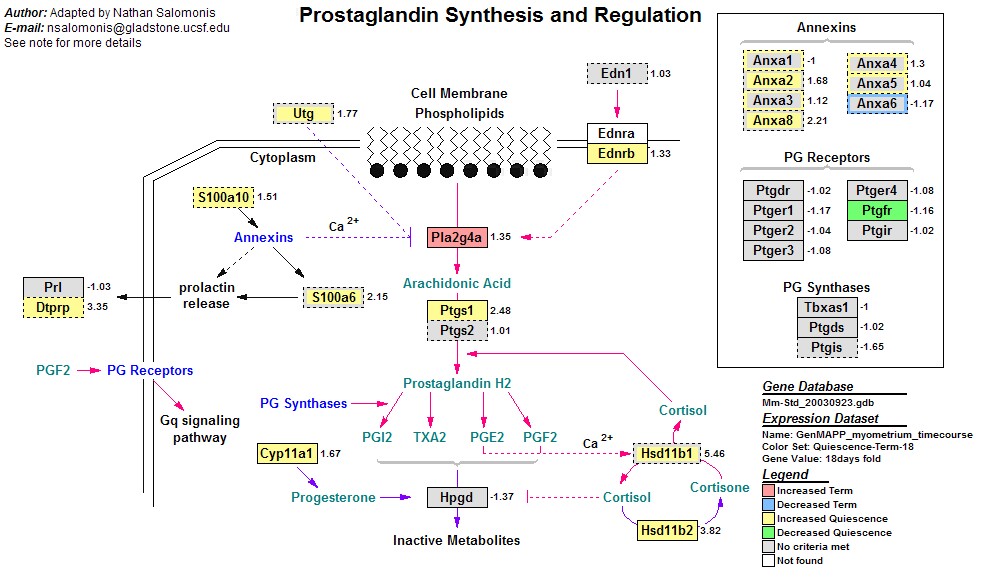
3 In fact, prostaglandins may have some anti-inflammatory action because they may downregulate some aspects of the inflammatory response. Indispensable roles of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in endothelium-dependent contractions. All mechanical modalities share a similar mechanism of actionnamely, some form of local pressure that stimulates the release of prostaglandins. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates the osteoclastic reabsorption of juxtaarticular bone its inhibition by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents may, therefore, retard the process of bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis and in other inflammatory processes. Current thought relegates prostaglandins to ‘a minor, mostly regulatory, role’ in ocular inflammation in primates. Prostaglandins are unsaturated carboxylic acids, consisting of of a 20 carbon skeleton that also contains a five member ring and are based upon the fatty acid, arachidonic acid. In addition, prostaglandin synthesis is also inhibited by glucocorticoids even though their mode of action may involve other effects as well. Inhibition of the vasodilator prostaglandins, prostaglandin E2 and prostacyclin, as well as the leukotrienes, may reduce their inflammatory effects in several disease states. Other groups of biologically active polyunsaturated fatty acid derivatives including the leukotrienes, are generally not inhibited by this class of drugs in the same concentration ranges. By reducing production of prostaglandins, NSAIDs help relieve the discomfort of fever and reduce inflammation and the associated pain. Aspirin and a large number of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs act primarily through the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
